Seksjon 1. Kapittel 14
single
 Utfordring: Bruk av iloc[]
Utfordring: Bruk av iloc[]
Sveip for å vise menyen
DataFrame-en du arbeider med:
Du kan også bruke negativ indeksering for å få tilgang til rader i DataFrame-en. Negativ indeksering starter fra slutten av DataFrame-en: indeks -1 peker på siste rad, -2 på nest siste, og så videre.
For å få tilgang til den syvende raden (som refererer til Latvia), kan du bruke enten indeks 6 eller -1.
123456import pandas countries_data = {'country' : ['Thailand', 'Philippines', 'Monaco', 'Malta', 'Sweden', 'Paraguay', 'Latvia'], 'continent' : ['Asia', 'Asia', 'Europe', 'Europe', 'Europe', 'South America', 'Europe'], 'capital':['Bangkok', 'Manila', 'Monaco', 'Valletta', 'Stockholm', 'Asuncion', 'Riga']} countries = pandas.DataFrame(countries_data) # Accessing to the seventh row using negative indexing print(countries.iloc[-1])
Å kjøre koden ovenfor vil returnere raden som er uthevet i bildet nedenfor:
Oppgave
Swipe to start coding
Du har fått en DataFrame kalt audi_cars.
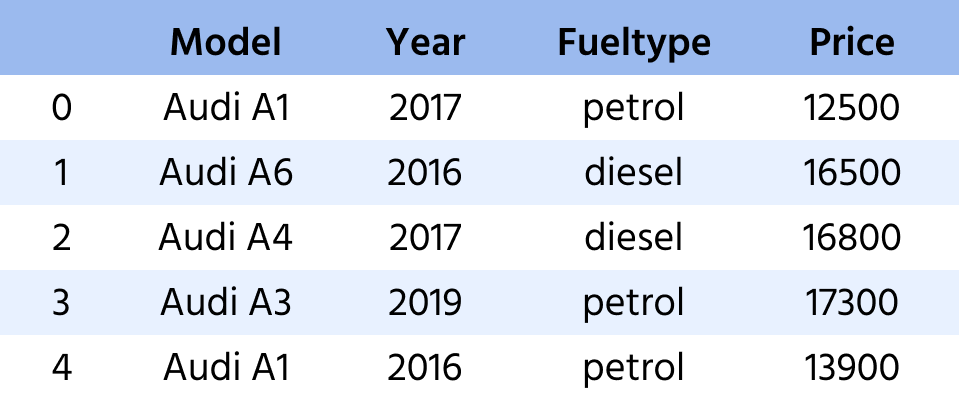
- Velg hele raden (alle kolonner) for modellen
'Audi A1'fra året 2017 og lagre den iaudi_A1_2017. - Gjør det samme for modellen
'Audi A1'fra året 2016 og lagre den iaudi_A1_2016. - Til slutt, velg modellen
'Audi A3'og lagre den iaudi_A3.
Løsning
Alt var klart?
Takk for tilbakemeldingene dine!
Seksjon 1. Kapittel 14
single
Spør AI
Spør AI

Spør om hva du vil, eller prøv ett av de foreslåtte spørsmålene for å starte chatten vår