Section 3. Chapter 8
single
 How Similar are the Results?
How Similar are the Results?
Swipe to show menu
Well done! Let's look at the last line charts you built in the previous chapter.
As you can see, only the ward linkage could catch the 'downward up to July' trend. Both results are different. But let's find out how different they are using the rand index.
Task
Swipe to start coding
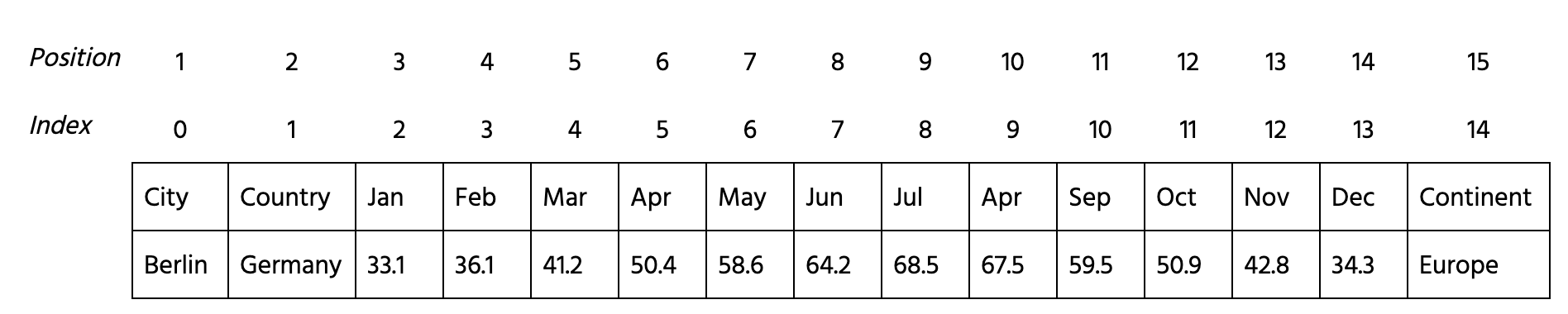
Compute the rand index to compare the results of using complete and ward linkages. Follow the next steps:
- Import functions needed:
rand_scorefromsklearn.metrics.AgglomerativeClusteringfromsklearn.cluster.
- Create two models
model_completeandmodel_wardperforming a hierarchical clustering with 4 clusters both and'complete'and'ward'linkages respectively. - Fit the 3-14 columns of
datato models and predict the labels. Save the labels formodel_completewithinlabels_completeand formodel_wardwithinlabels_ward. - Compute the rand index using
labels_completeandlabels_ward.
Solution
Everything was clear?
Thanks for your feedback!
Section 3. Chapter 8
single
Ask AI
Ask AI

Ask anything or try one of the suggested questions to begin our chat